| 基站布置 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Time Limit: 1000 MS | Memory Limit: 1000 KB | |
Description
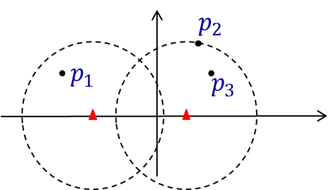
海面上有一些船需要与陆地进行通信,需要在海岸线上布置一些基站。现将问题抽象为,在x轴上方,给出n条船的 坐标p1,p2,…,pn,其中pi=(xi,yi),0≤yi≤d, 1≤i≤n,在x轴安放的基站可以覆盖半径为d的区域内的所有船只, 问在x轴至少要安放几个基站才可以将x轴上方的船只都覆盖到。
Input
第一行输入m表示有m组测试. 每组测试首先输入两个整数n(n<=10000)和d,接下来输入n个整数坐标(x,y),其中0≤y≤d. 黑色, 其中0和1的个数分别为n个.
Output
对每组测试数据输出所需最少基站个数. 提示: 判断两点距离是否小于d可能需要考虑精度损失, 建议使用 (x1-x2)*(x1-x2) + (y1-y2)*(y1-y2) - d*d <= 1e-10 而非 (x1-x2)*(x1-x2) + (y1-y2)*(y1-y2) <= d*d
Sample Input
2 3 2 0 1 2 1 3 2 4 4 0 1 1 1 2 1 3 2
Sample Output
2
1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
struct pos_t {
double x, y;
double rsect;
} pos[10010];
int cover[10010];
int n;
double d;
const double minINF = 0.00000000001;//浮点误差
int cmp(const void *a, const void *b) {
pos_t *ta, *tb;
ta = (pos_t *)a;
tb = (pos_t *)b;
double temp = ta->rsect-tb->rsect;
if(-minINF<=temp && temp<=minINF) {//浮点数比较注意预留一定的精度判断
//if(temp == 0) {
return 0;
}
else if (temp < 0) {
return -1;
}
else {
return 1;
}
}
int solve() {
scanf("%d%lf", &n, &d);
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
scanf("%lf%lf", &pos[i].x, &pos[i].y);
pos[i].rsect = pos[i].x + sqrt(d*d-pos[i].y*pos[i].y);
}
memset(cover, 0, sizeof(cover));
qsort(pos, n, sizeof(pos_t), cmp);
int count = 0;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
if(cover[i] == 1) {
continue;
}
count = count + 1;
for(int j=i; j<n; j++) {
if(pos[j].rsect-pos[i].rsect > 2*d) {
break;
}
if(cover[j]==1) {
continue;
}
//下面也需要注意浮点误差
double temp = (pos[j].x-pos[i].rsect)*(pos[j].x-pos[i].rsect) + pos[j].y*pos[j].y - d*d;
if(temp<=minINF) {
cover[j] = 1;
}
}
}
printf("%d\n", count);
}
int main() {
int m;
scanf("%d", &m);
for(int i=0; i<m; i++) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}